We
recently identified five new three-finger toxins from
king cobra venom u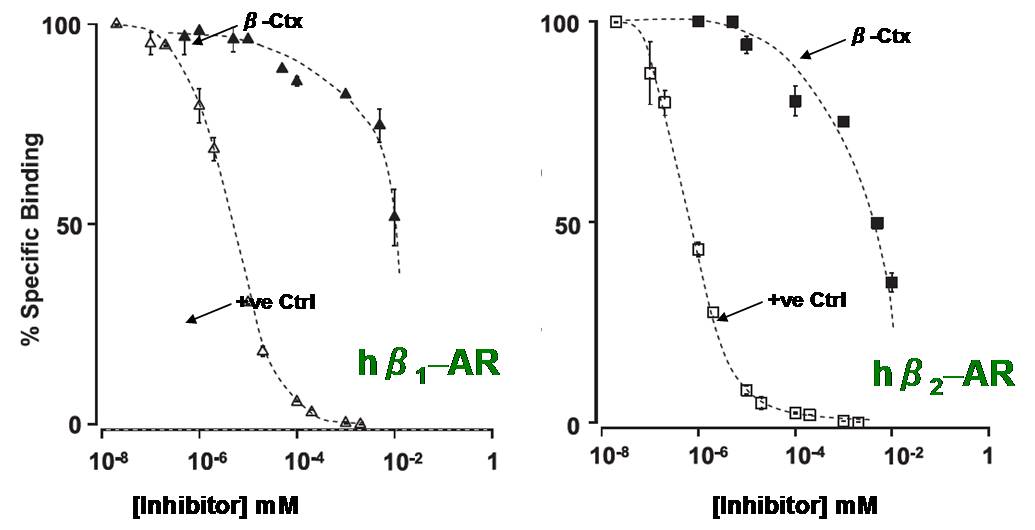 sing cDNA library. We also purified
these proteins from the crude venom using
chromatographic techniques. One of these proteins induced decreased heart rate as well as difficulty in
breathing in mice. In contrast to classical cardiotoxins
which increase the heart rate, this novel protein
decreased the heart rate in anesthetized rats as well as
in isolated rat hearts. Further studies showed that this
protein binds to β1-
and β2-
adrenergic receptors, and hence this novel protein was
named as
β -cardiotoxin. This is the first exogenous beta-blocker from plant,
animal or microbial origin.
sing cDNA library. We also purified
these proteins from the crude venom using
chromatographic techniques. One of these proteins induced decreased heart rate as well as difficulty in
breathing in mice. In contrast to classical cardiotoxins
which increase the heart rate, this novel protein
decreased the heart rate in anesthetized rats as well as
in isolated rat hearts. Further studies showed that this
protein binds to β1-
and β2-
adrenergic receptors, and hence this novel protein was
named as
β -cardiotoxin. This is the first exogenous beta-blocker from plant,
animal or microbial origin.

