|
This
is a family of nonenzymatic polypeptides containing 60-74
amino acid residues. They contain four or five disulfide
bridges of which four are conserved in all the members.
Consequently, all proteins of this family show similar pattern
of protein folding: three β-stranded loops extending from
a central core containing the four conserved disulfide bridges.
Because of their appearance, this family of proteins is
called the three-finger toxin family.
Currently,
we are working on the following toxins:
Candoxin,
a non-conventional 3FTx, isolated from Bungarus candidus
venom is the first reversible neurotoxin which binds to
peripheral nAChRs at nanomolar concentrations. This monomeric
toxin irreversibly binds to α7 nAChRs despite the absence
of key structural and functional determinants that are important
for the recognition of α7 nAChRs.
Denmotoxin,
isolated from Boiga dendrophila (Mangrove Catsnake) venom,
is the first species-specific neurotoxin. It irreversibly
blocks neurotransmission at chick neuromuscular junctions,
but reversibly blocks it in mouse neuromuscular junction.
This monomeric toxin shows 100-fold higher affinity to chick
nAChRs compared to mouse receptors. Thus, we would like
to understand the structure function relationship of the
toxin and delineate the active site that is specific of
avian ACh receptors.
Haditoxin,
isolated from the venom of Ohiophagus hannah (King cobra),
is the first homodimer short-chain neurotoxin. It exhibited
novel pharmacology with antagonism towards muscle and neuronal
nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs), with highest
affinity for α7-nAChRs. It is the first short-chain neurotoxin
that binds to neuronal receptors. Interestingly, it irreversibly
blocks neurotransmission at rat neuromuscular junctions,
but reversibly blocks it in chick neuromuscular junctions
and hence its species specificity is reversed compared to
denmotoxin and hence interesting to delineate its active
site with respect to active site of denmotoxin.
Drysdalin
is the longest 3FTx (87aa) among all the 3FTx found in Drysdalia
coronoides. It blocks both peripheral and neuronal receptors
inspite of lacking many functionally conserved residues.
Thus in order to understand the structure function relationship
mutants of dyrsdalin will be tested for their function.
Our
contributions are:
-
We have solved structure-function relationships of several
toxins of three-finger family. We have identified the
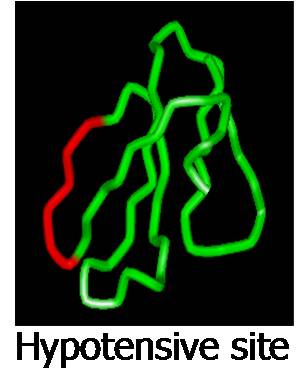
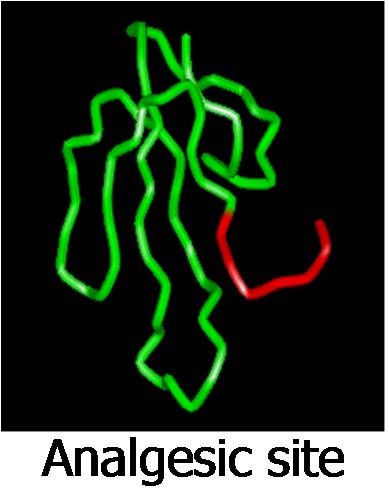
cytolytic, hypotensive and analgesic sites in this family
of toxins. The hypotensive and analgesic peptides are
covered under US patents.
-
Determined the mechanism of antiplatelet effect of a
cardiotoxin. We showed that cytolytic activity of this
cardiotoxin is responsible for the antiplatelet effect.
-
We have recently purified several novel members of this
family. We have been studying their 3D structures and
biological properties.
-
We have determined the 3D structures of bucandin, bucain
and bungatoxin using X-ray diffraction and NMR techniques.
Their biological properties are under investigation.
-
Candoxin is a unique toxin; it binds reversibly to the
peripheral muscular acetylcholine receptor, but binds
irreversibly to the neuronal α 7 acetylcholine receptor.
We have also determined its 3D structure.
-
Colubritoxin is the first toxin isolated from a ‘non venomous’ snake (Coelognathus
radiatus). It is structurally similar to neurotoxin
isolated from cobra venom. It reversibly blocks the
peripheral acetylcholine receptor.
-
We isolated and characterized two bird-specific postsynaptic
neurotoxins from Boiga venoms. Denmotoxin is an irreversible
inhibitor
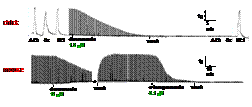 of
neurotransmission in chick biventer cervicis muscle
where as it is a highly reversible blocker of neurotransmission
in mouse hemidiaphragm preparations. Similarly, irditoxin
is highly toxic to chicks but not-so-toxic to mice.
Denmotoxin is a monomer where as irditoxin is a heterodimer
held together by a disulfide bond. We have determined
the 3D structures of both these toxins. of
neurotransmission in chick biventer cervicis muscle
where as it is a highly reversible blocker of neurotransmission
in mouse hemidiaphragm preparations. Similarly, irditoxin
is highly toxic to chicks but not-so-toxic to mice.
Denmotoxin is a monomer where as irditoxin is a heterodimer
held together by a disulfide bond. We have determined
the 3D structures of both these toxins.
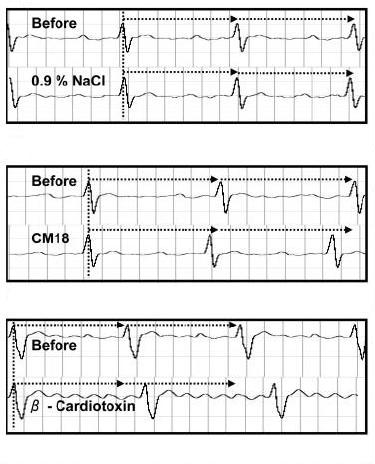
-
We isolated and characterized a new class of three-finger
toxins that bind to β- adrenergic receptors and decrease
the heart rate. These are the first natural, exogenous
beta-blockers. They are named as β- cardiotoxins. Its
3D structure and structure-function relationships are
under investigation.
Key
Publications
|