|
|
Snake Venom Prothrombin Activators
|
Prothrombin activators are an important group of procoagulant (inducing blood clotting) proteins isolated from snake venom. Our contributions to this group of proteins are as follows.
-
We purified, characterized and completed the amino acid sequence of snake venom prothrombin activators (group D) that are structurally and functionally similar to mammalian blood coagulation factor Xa. Its procoagulant properties and its substrate specificity can be exploited and hence we have applied for the provisional patent protection for this group of proteins isolated from venoms. This is licensed to an Australian company.
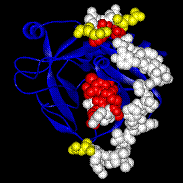
We have examined the structure-function relationships of group D prothrombin activators. Based on their structure and affinity to bovine factor Va, we developed new class of anticoagulant peptides that interfere in the interaction between factor Xa and factor Va and inhibit the formation of the prothrombinase complex (Patents pending).
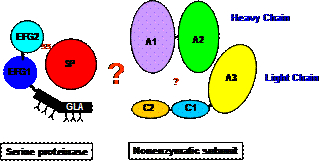
-
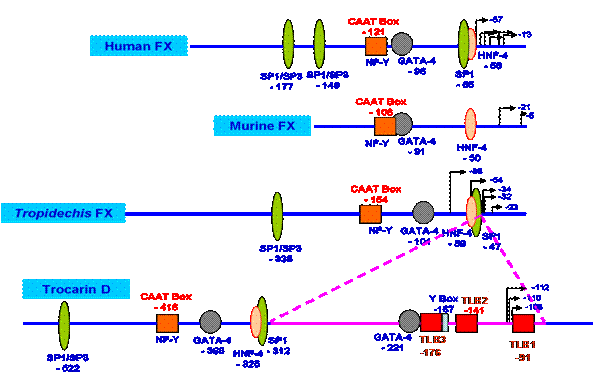
We identified an intermediate in the evolution of the factor Xa-like enzymatic subunit of prothrombin activators.
|
Key
Publications
|
|

